
MySQL Workbench is an integrated development environment (IDE) for MySQL database management and administration. It provides a graphical user interface (GUI) that allows users to design, develop, and administer MySQL databases efficiently.
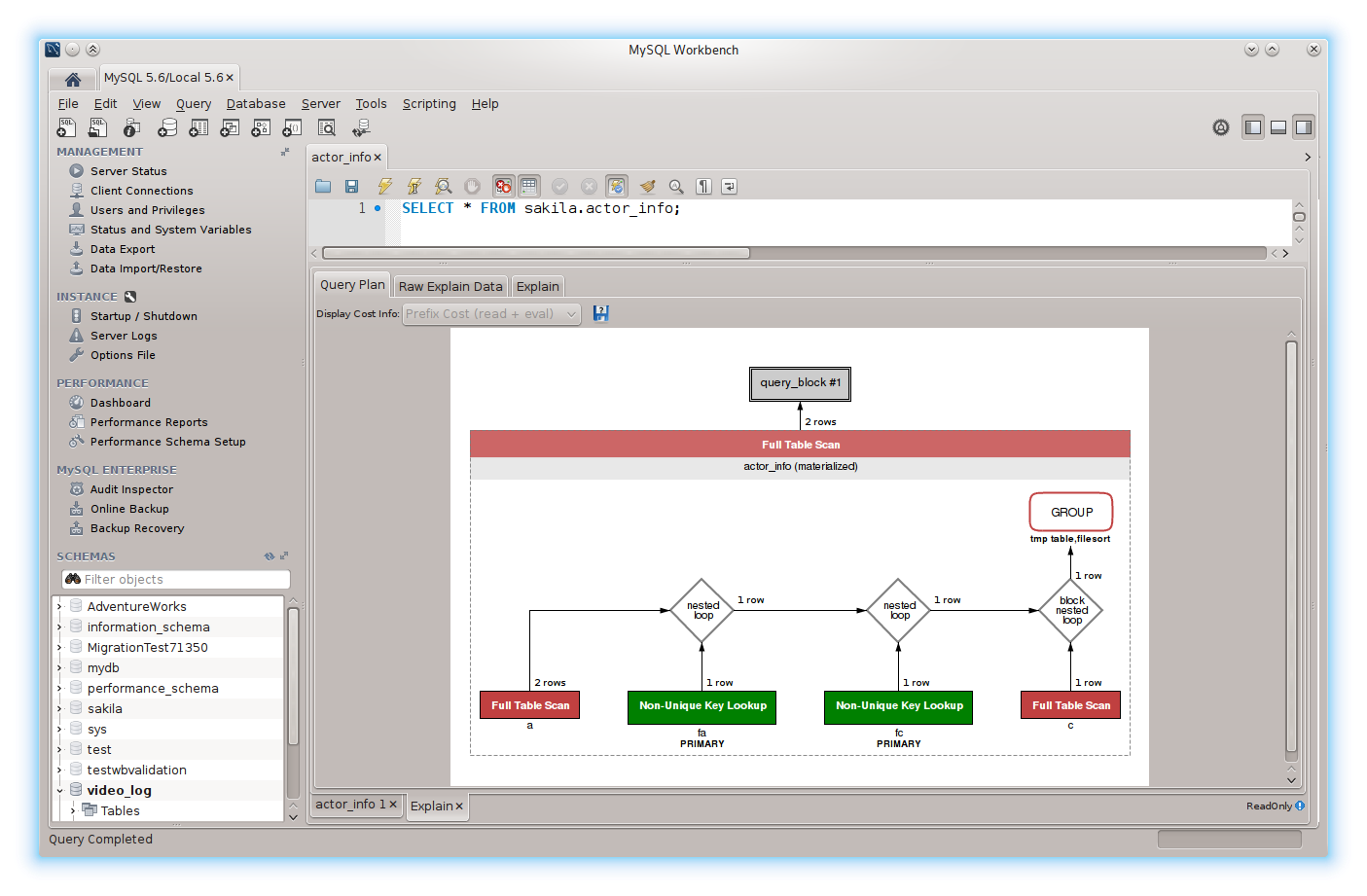
MySQL Workbench – Here are some key features and functionalities of MySQL Workbench:
- Database Design: MySQL Workbench enables users to visually design and model databases using a drag-and-drop interface. It supports the creation of database entities such as tables, views, indexes, and relationships, allowing users to define the structure and schema of their databases easily.
- SQL Development: Users can write, edit, and execute SQL queries, scripts, and stored procedures directly within MySQL Workbench. It offers syntax highlighting, code completion, and query formatting features to enhance productivity and accuracy when working with SQL code.
- Database Administration: MySQL Workbench provides tools for managing and administering MySQL database servers. Users can perform tasks such as creating and managing database connections, user accounts, and privileges, as well as monitoring server status, performance metrics, and system variables.
- Data Modeling: The tool offers reverse engineering capabilities, allowing users to generate database models from existing schemas or SQL scripts. It also supports forward engineering, enabling users to generate SQL scripts from database models for deployment and synchronization purposes.
- Database Migration: MySQL Workbench includes migration tools that facilitate the migration of databases from other platforms or database management systems (DBMS) to MySQL. It supports the migration of schemas, tables, data, and stored procedures from various sources, simplifying the process of transitioning to MySQL.
- Performance Analysis: MySQL Workbench provides performance monitoring and analysis features to help users identify and diagnose performance issues within their MySQL databases. It offers visual tools for analyzing query execution plans, identifying slow queries, and optimizing database performance.
- Backup and Restore: Users can perform database backup and restoration tasks directly within MySQL Workbench. It supports full, incremental, and partial backups, as well as point-in-time recovery, allowing users to protect their data and restore it to a specific state in case of data loss or corruption.

Overall, MySQL Workbench is a powerful and versatile tool for MySQL database development, administration, and management. It is widely used by database administrators, developers, and data analysts to streamline database-related tasks and workflows in both small-scale and enterprise-level environments.

MySQL Server Management involves overseeing the installation, configuration, maintenance, and optimization of MySQL database servers to ensure they operate efficiently and securely.
Here’s a breakdown of what MySQL Server Management typically entails:
- Installation: Setting up MySQL server software on a host machine. This involves downloading the appropriate MySQL distribution for your operating system, running the installer, and configuring basic settings such as port number, root password, and data directory.
- Configuration: Fine-tuning MySQL server settings to optimize performance, security, and resource usage. This includes adjusting parameters such as buffer sizes, cache settings, connection limits, and logging options based on the specific requirements of your application and hardware resources.
- Security Management: Implementing security measures to protect the MySQL server from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats. This involves setting up user accounts with appropriate privileges, enabling encryption for data transmission and storage, configuring firewall rules, and regularly applying security patches and updates.
- Backup and Recovery: Establishing backup and recovery procedures to safeguard critical data in case of hardware failures, software errors, or accidental data loss. This typically involves scheduling regular backups of databases and transaction logs, verifying backup integrity, and testing restoration procedures to ensure data can be recovered promptly when needed.
- Monitoring and Performance Tuning: Monitoring MySQL server performance metrics such as CPU usage, memory consumption, disk I/O, and query execution times to identify bottlenecks, resource contention, and performance issues. Performance tuning involves optimizing database schemas, query design, indexing strategies, and server configurations to improve overall system performance and responsiveness.
- High Availability and Scalability: Implementing strategies to ensure high availability and scalability of MySQL database servers to meet growing demands and minimize downtime. This may involve setting up replication, clustering, or sharding solutions to distribute workload across multiple servers, as well as implementing failover mechanisms to automatically switch to standby servers in case of failures.
- Database Maintenance: Performing routine maintenance tasks such as database reorganization, index optimization, and table optimization to reclaim disk space, improve query performance, and prevent fragmentation. This also includes monitoring disk space usage, database growth, and resource utilization to prevent capacity issues and plan for future expansion.
Overall, MySQL Server Management is a critical aspect of maintaining the health, performance, and reliability of MySQL database servers in production environments. It requires a combination of technical expertise, monitoring tools, and best practices to ensure optimal database performance and data integrity.
