Understanding SSL: Key Differences Between Free and Paid Certificates
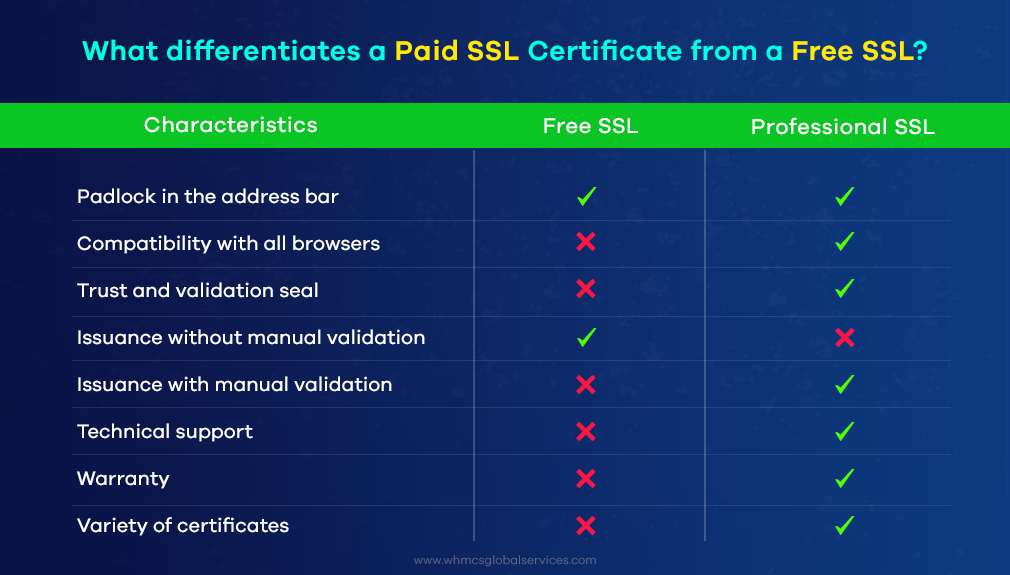
When considering SSL certificates for securing your website, you’ll encounter both free and paid options. Understanding the differences between these types can help you choose the right one for your needs. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences between free and paid certificates:
1. Cost
- Free Certificates:
- Price: As the name suggests, free certificates are available at no cost.
- Example Providers: Let’s Encrypt, Cloudflare, and some web hosting services offer free options.
- Paid Certificates:
- Price: Paid certificates come with various pricing tiers depending on the level of validation and coverage.
- Example Providers: Comodo (now Sectigo), DigiCert, Symantec, GeoTrust, and Thawte.

2. Validation Types
- Free SSL Certificates:
- Validation Level: Most free certificates are Domain Validation (DV) certificates. They only verify that you own the domain, not your identity.
- Usage: Suitable for personal websites, blogs, and small business sites that don’t require higher levels of trust.
- Paid SSL Certificates:
- Validation Levels: Paid certificates offer various validation levels:
- Domain Validation (DV): Confirms domain ownership.
- Organization Validation (OV): Verifies the legitimacy of the organization behind the domain.
- Extended Validation (EV): Provides the highest level of validation, displaying the organization’s name in the browser’s address bar, which enhances trust.
- Usage: Ideal for e-commerce sites, financial institutions, and larger organizations that need to establish greater trust with their users.
- Validation Levels: Paid certificates offer various validation levels:
3. Warranty and Support
- Free SSL Certificates:
- Warranty: Generally, free certificates do not offer a warranty.
- Support: Limited customer support. Help is usually available through community forums or online documentation.
- Paid SSL Certificates:
- Warranty: Paid certificates often come with a warranty that provides financial protection against potential data breaches or certificate failures.
- Support: Includes dedicated customer support, often with 24/7 availability and assistance with installation and troubleshooting.
4. Trust and Credibility
- Free SSL Certificates:
- Trust Level: Generally, free certificates are trusted by most modern browsers and systems. However, some users may perceive paid certificates as more credible due to the validation process.
- Paid SSL Certificates:
- Trust Level: Paid certificates, especially EV certificates, are often associated with higher trust levels due to their thorough validation process. This can be beneficial for building customer trust, especially for financial transactions and sensitive data.
5. Features and Customization
- Free SSL Certificates:
- Features: Basic encryption and functionality. Limited to single-domain or subdomain coverage.
- Customization: Limited options for customization and additional features.
- Paid SSL Certificates:
- Features: Can offer additional features such as wildcard coverage (securing multiple subdomains), multi-domain support, and additional encryption algorithms.
- Customization: More options for certificate types and configurations.
6. Renewal and Management
- Free SSL Certificates:
- Renewal: Typically have shorter validity periods (e.g., 90 days) and require more frequent renewals. Automated renewal is often available.
- Management: Basic management tools, often provided by the certificate issuer or integrated into your hosting control panel.
- Paid SSL Certificates:
- Renewal: Generally have longer validity periods (e.g., 1 to 2 years) with options for auto-renewal.
- Management: More comprehensive management tools and interfaces for handling certificate renewals, reissues, and installations.
Conclusion
Both free and paid SSL certificates provide encryption for securing data transmitted between a web server and a browser. The choice between them depends on your specific needs:
- Free Certificates: Ideal for personal websites, blogs, or small projects where budget constraints are a concern.
- Paid Certificates: Better suited for business-critical applications, e-commerce sites, and organizations that require higher levels of validation, additional features, and dedicated support.
